This post takes up from two previous posts (part 1; part 2), asking just what do we (we economists) really know about how interest rates affect inflation. Today, what does contemporary economic theory say?
As you may recall, the standard story says that the Fed raises interest rates; inflation (and expected inflation) don't immediately jump up, so real interest rates rise; with some lag, higher real interest rates push down employment and output (IS); with some more lag, the softer economy leads to lower prices and wages (Phillips curve). So higher interest rates lower future inflation, albeit with "long and variable lags."
Higher interest rates -> (lag) lower output, employment -> (lag) lower inflation.
In part 1, we saw that it's not easy to see that story in the data. In part 2, we saw that half a century of formal empirical work also leaves that conclusion on very shaky ground.
As they say at the University of Chicago, "Well, so much for the real world, how does it work in theory?" That is an important question. We never really believe things we don't have a theory for, and for good reason. So, today, let's look at what modern theory has to say about this question. And they are not unrelated questions. Theory has been trying to replicate this story for decades.
The answer: Modern (anything post 1972) theory really does not support this idea. The standard new-Keynesian model does not produce anything like the standard story. Models that modify that simple model to achieve something like result of the standard story do so with a long list of complex ingredients. The new ingredients are not just sufficient, they are (apparently) necessary to produce the desired dynamic pattern. Even these models do not implement the verbal logic above. If the pattern that high interest rates lower inflation over a few years is true, it is by a completely different mechanism than the story tells.
I conclude that we don't have a simple economic model that produces the standard belief. ("Simple" and "economic" are important qualifiers.)
The simple new-Keynesian model
The central problem comes from the Phillips curve. The modern Phillips curve asserts that price-setters are forward-looking. If they know inflation will be high next year, they raise prices now. So
Inflation today = expected inflation next year + (coefficient) x output gap.
\[\pi_t = E_t\pi_{t+1} + \kappa x_t\](If you know enough to complain about \(\beta\approx0.99\) in front of \(E_t\pi_{t+1}\) you know enough that it doesn't matter for the issues here.)
Now, if the Fed raises interest rates, and if (if) that lowers output or raises unemployment, inflation today goes down.
The trouble is, that's not what we're looking for. Inflation goes down today, (\(\pi_t\))relative to expected inflation next year (\(E_t\pi_{t+1}\)). So a higher interest rate and lower output correlate with inflation that is rising over time.
Here is a concrete example:
The plot is the response of the standard three equation new-Keynesian model to an \(\varepsilon_1\) shock at time 1:\[\begin{align} x_t &= E_t x_{t+1} - \sigma(i_t - E_t\pi_{t+1}) \\ \pi_t & = \beta E_t \pi_{t+1} + \kappa x_t \\ i_t &= \phi \pi_t + u_t \\ u_t &= \eta u_{t-1} + \varepsilon_t. \end{align}\] Here \(x\) is output, \(i\) is the interest rate, \(\pi\) is inflation, \(\eta=0.6\), \(\sigma=1\), \(\kappa=0.25\), \(\beta=0.95\), \(\phi=1.2\).
In this plot, higher interest rates are said to lower inflation. But they lower inflation immediately, on the day of the interest rate shock. Then, as explained above, inflation rises over time.
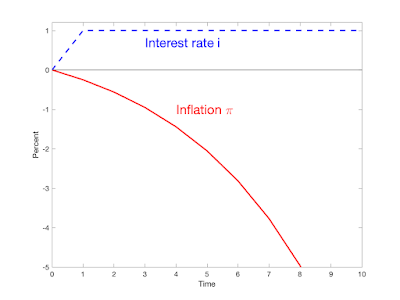
In the standard view, and the empirical estimates from the last post, a higher interest rate has no immediate effect, and then future inflation is lower. See plots in the last post, or this one from Romer and Romer's 2023 summary:
Inflation jumping down and then rising in the future is quite different from inflation that does nothing immediately, might even rise for a few months, and then starts gently going down.
You might even wonder about the downward jump in inflation. The Phillips curve makes it clear why current inflation is lower than expected future inflation, but why doesn't current inflation stay the same, or even rise, and expected future inflation rise more? That's the "equilibrium selection" issue. All those paths are possible, and you need extra rules to pick a particular one. Fiscal theory points out that the downward jump needs a fiscal tightening, so represents a joint monetary-fiscal policy. But we don't argue about that today. Take the standard new Keynesian model exactly as is, with passive fiscal policy and standard equilibrium selection rules. It predicts that inflation jumps down immediately and then rises over time. It does not predict that inflation slowly declines over time.
This is not a new issue. Larry Ball (1994) first pointed out that the standard new Keynesian Phillips curve says that output is high when inflation is high relative to expected future inflation, that is when inflation is declining. Standard beliefs go the other way: output is high when inflation is rising.
The IS curve is a key part of the overall prediction, and output faces a similar problem. I just assumed above that output falls when interest rates rise. In the model it does; output follows a path with the same shape as inflation in my little plot. Output also jumps down and then rises over time. Here too, the (much stronger) empirical evidence says that an interest rate rise does not change output immediately, and output then falls rather than rises over time. The intuition has even clearer economics behind it: Higher real interest rates induce people to consume less today and more tomorrow. Higher real interest rates should go with higher, not lower, future consumption growth. Again, the model only apparently reverses the sign by having output jump down before rising.
Key issues
How can we be here, 40 years later, and the benchmark textbook model so utterly does not replicate standard beliefs about monetary policy?
One answer, I believe, is confusing adjustment to equilibrium with equilibrium dynamics. The model generates inflation lower than yesterday (time 0 to time 1) and lower than it otherwise would be (time 1 without shock vs time 1 with shock). Now, all economic models are a bit stylized. It's easy to say that when we add various frictions, "lower than yesterday" or "lower than it would have been" is a good parable for "goes down over time." If in a simple supply and demand graph we say that an increase in demand raises prices instantly, we naturally understand that as a parable for a drawn out period of price increases once we add appropriate frictions.
But dynamic macroeconomics doesn't work that way. We have already added what was supposed to be the central friction, sticky prices. Dynamic economics is supposed to describe the time-path of variables already, with no extra parables. If adjustment to equilibrium takes time, then model that.
The IS and Phillips curve are forward looking, like stock prices. It would make little sense to say "news comes out that the company will never make money, so the stock price should decline gradually over a few years." It should jump down now. Inflation and output behave that way in the standard model.
A second confusion, I think, is between sticky prices and sticky inflation. The new-Keynesian model posits, and a huge empirical literature examines, sticky prices. But that is not the same thing as sticky inflation. Prices can be arbitrarily sticky and inflation, the first derivative of prices, can still jump. In the Calvo model, imagine that only a tiny fraction of firms can change prices at each instant. But when they do, they will change prices a lot, and the overall price level will start increasing right away. In the continuous-time version of the model, prices are continuous (sticky), but inflation jumps at the moment of the shock.
The standard story wants sticky inflation. Many authors explain the new-Keynesian model with sentences like "the Fed raises interest rates. Prices are sticky, so inflation can't go up right away and real interest rates are higher." This is wrong. Inflation can rise right away. In the standard new-Keynesian model it does so with \(\eta=1\), for any amount of price stickiness. Inflation rises immediately with a persistent monetary policy shock.
Just get it out of your heads. The standard model does not produce the standard story.
The obvious response is, let's add ingredients to the standard model and see if we can modify the response function to look something like the common beliefs and VAR estimates. Let's go.
Adaptive expectations
We can reproduce standard beliefs about monetary policy with thoroughly adaptive expectations, in the 1970s ISLM form. I think this is a large part of what most policy makers and commenters have in mind.
Modify the above model to leave out the dynamic part of the intertemporal substitution equation, to just say in rather ad hoc way that higher real interest rates lower output, and specify that the expected inflation that drives the real rate and that drives pricing decisions is mechanically equal to previous inflation, \(E_t \pi_{t+1} = \pi_{t-1}\). We get \[ \begin{align} x_t &= -\sigma (i_t - \pi_{t-1}) \\ \pi_t & = \pi_{t-1} + \kappa x_t .\end{align}\] We can solve this sytsem analytically to \[\pi_t = (1+\sigma\kappa)\pi_{t-1} - \sigma\kappa i_t.\]
Here's what happens if the Fed permanently raises the interest rate. Higher interest rates send
future inflation down. (\(\kappa=0.25,\ \sigma=1.\)) Inflation eventually spirals away, but central banks don't leave interest rates alone forever. If we add a Taylor rule response \(i_t = \phi \pi_t + u_t\), so the central bank reacts to the emerging spiral, we get this response to a permanent monetary policy
disturbance \(u_t\):
The higher interest rate sets off a deflation spiral. But the Fed quickly follows inflation down to stabilize the situation. This is, I think, the conventional story of the 1980s.
In terms of ingredients, an apparently minor change of index from \(E_t \pi_{t+1}\) to \(\pi_{t-1}\) is in fact a big change. It means directly that higher output comes with increasing inflation, not decreasing inflation, solving Ball's puzzle. The change basically changes the sign of output in the Phillips curve.
Again, it's not really all in the Phillips curve. This model with rational expectations in the IS equation and adaptive in the Phillips curve produces junk. To get the result you need adaptive expectations everywhere.
The adaptive expectations model gets the desired result by changing the basic sign and stability properties of the model. Under rational expectations the model is stable; inflation goes away all on its own under an interest rate peg. With adaptive expectations, the model is unstable. Inflation or deflation spiral away under an interest rate peg or at the zero bound. The Fed's job is like balancing a broom upside down. If you move the bottom (interest rates) one way, the broom zooms off the other way. With rational expectations, the model is stable, like a pendulum. This is not a small wrinkle designed to modify dynamics. This is major surgery. It is also a robust property: small changes in parameters do not change the dominant eigenvalue of a model from over one to less than one.
A more refined way to capture how Fed officials and pundits think and talk might be called "temporarily fixed expectations." Policy people do talk about the modern Phillips curve; they say inflation depends on inflation expectations and employment. Expectations are not mechanically adaptive. Expectations are a third force, sometimes "anchored," and amenable to manipulation by speeches and dot plots. Crucially, in this analysis, expected inflation does not move when the Fed changes interest rates. Expectations are then very slowly adaptive, if inflation is persistent, or if there is a more general loss of faith in "anchoring." In the above new-Keynesian model graph, at the minute the Fed raises the interest rate, expected inflation jumps up to follow the graph's plot of the model's forecast of inflation.
As a simple way to capture these beliefs, suppose expectations are fixed or "anchored" at \(\pi^e\). Then my simple model is \[\begin{align}x_t & = -\sigma(i_t - \pi^e) \\ \pi_t & = \pi^e + \kappa x_t\end{align}\]so \[\pi_t = \pi^e - \sigma \kappa (i_t - \pi^e).\] Inflation is expected inflation, and lowered by higher interest rates (last - sign). But those rates need only be higher than the fixed expectations; they do not need to be higher than past rates as they do in the adaptive expectations model. That's why the Fed thinks 3% interest rates with 5% inflation is still "contractionary"--expected inflation remains at 2%, not the 5% of recent adaptive experience. Also by fixing expectations, I remove the instability of the adaptive expectations model... so long as those expectations stay anchored. The Fed recognizes that eventually higher inflation moves the expectations, and with a belief that is adaptive, they fear that an inflation spiral can still break out.
Even this view does not give us any lags, however. The Fed and commenters clearly believe that higher real interest rates today lower output next year, not immediately; and they believe that lower output and employment today drive inflation down in the future, not immediately. They believe something like \[\begin{align}x_{t+1} &= - \sigma(i_t - \pi^e) \\ \pi_{t+1} &= \pi^e + \kappa x_t.\end{align}\]
But now we're at the kind of non-economic ad-hockery that the whole 1970s revolution abandoned. And for a reason: Ad hoc models are unstable, regimes are always changing. Moreover, let me remind you of our quest: Is there a simple economic model of monetary policy that generates something like the standard view? At this level of ad-hockery you might as well just write down the coefficients of Romer and Romer's response function and call that the model of how interest rates affect inflation.
Academic economics gave up on mechanical expectations and ad-hoc models in the 1970s. You can't publish a paper with this sort of model. So when I mean a "modern" model, I mean rational expectations, or at least the consistency condition that the expectations in the model are not fundamentally different from forecasts of the model. (Models with explicit learning or other expectation-formation frictions count too.)
It's easy to puff about people aren't rational, and looking out the window lots of people do dumb things. But if we take that view, then the whole project of monetary policy on the proposition that people are fundamentally unable to learn patterns in the economy, that a benevolent Federal Reserve can trick the poor little souls into a better outcome. And somehow the Fed is the lone super-rational actor who can avoid all those pesky behavioral biases.
We are looking for the minimum necessary ingredients to describe the basic signs and function of monetary policy. A bit of irrational or complex expectation formation as icing on the cake, a possible sufficient ingredient to produce quantitatively realistic dynamics, isn't awful. But it would be sad if irrational expectations or other behavior is a necessary ingredient to get the most basic sign and story of monetary policy right. If persistent irrationality is a central necessary ingredient for the basic sign and operation of monetary policy -- if higher interest rates will raise inflation the minute people smarten up; if there is no simple supply and demand, MV=PY sensible economics underlying the basic operation of monetary policy; if it's all a conjuring trick -- that should really weaken our faith in the whole monetary policy project.
Facts help, and we don't have to get religious about it. During the long zero bound, the same commentators and central bankers kept warning about a deflation spiral, clearly predicted by this model. It never happened. Interest rates below inflation from 2021 to 2023 should have led to an upward inflation spiral. It never happened -- inflation eased all on its own with interest rates below inflation.Getting the desired response to interest rates by making the model unstable isn't tenable whether or not you like the ingredient. Inflation also surged in the 1970s faster than adaptive expectations came close to predicting, and fell faster in the 1980s. The ends of many inflations come with credible changes in regime.
There is a lot of work now desperately trying to fix new-Keynesian models by making them more old-Keynesian, putting lagged inflation in the Phillips curve, current income in the IS equation, and so forth. Complex learning and expectation formation stories replace the simplistic adaptive expectations here. As far as I can tell, to the extent they work they largely do so in the same way, by reversing the basic stability of the model.
Modifying the new-Keynesian model
The alternative is to add ingredients to the basic new-Keynesian model, maintaining its insistence on real "micro-founded" economics and forward-looking behavior, and describing explicit dynamics as the evolution of equilibrium quantities.
Christiano Eichenbaum and Evans (2005) is one of the most famous examples. Recall these same authors created the first most influential VAR that gave the "right" answer to the effects of monetary policy shocks. This paper modifies the standard new-Keynesian model with a specific eye to matching impulse response functions. The want to match all impulse-responses, with a special focus on output. When I started asking my young macro colleagues for a standard model which produces the desired response shape, they still cite CEE first, though it's 20 years later. That's quite an accomplishment. I'll look at it in detail, as the general picture is the same as many other models that achieve the desired result.
Here's their bottom line response to a monetary policy shock: (Figure from the 2018 Christiano Eichenbaum and Trabandt
Journal of Economic Perspectives summary paper.)
The solid line is the VAR point estimate and gray shading is the 95% confidence band. The solid blue line is the main model. The dashed line is the model with only price stickiness, to emphasize the importance of wage stickiness. The shock happens at time 0. Notice the funds rate line that jumps down at that date. That the other lines do not move at time 0 is a result. I graphed the response to a time 1 shock above.
That's the answer, now what's the question? What ingredients did they add above the textbook model to reverse the basic sign and jump problem and to produce these pretty pictures? Here is a partial list:
- Habit formation. The utility function is \(log(c_t - bc_{t-1})\).
- A capital stock with adjustment costs in investment. Adjustment costs are proportional to investment growth, \([1-S(i_t/i_{t-1})]i_t\), rather than the usual formulation in which adjustment costs are proportional to the investment to capital ratio \(S(i_t/k_t)i_t\).
- Variable capital utilization. Capital services \(k_t\) are related to the capital stock \(\bar{k}t\) by \(k_t = u_t \bar{k}_t\). The utilization rate \(u_t\) is set by households facing an upward sloping cost \(a(u_t)\bar{k}_t\).
- Calvo pricing with indexation: Firms randomly get to reset prices, but firms that aren't allowed to reset prices do automatically raise prices at the rate of inflation.
- Prices are also fixed for a quarter. Technically, firms must post prices before they see the period's shocks.
- Sticky wages, also with indexation. Households are monopoly suppliers of labor, and set wages Calvo-style like firms. (Later papers put all households into a union which does the wage setting.) Wages are also indexed; Households that don't get to reoptimize their wage still raise wages following inflation.
- Firms must borrow working capital to finance their wage bill a quarter in advance, and thus pay a interest on the wage bill.
- Money in the utility function, and money supply control. Monetary policy is a change in the money growth rate, not a pure interest rate target.
Whew! But which of these ingredients are necessary, and which are just sufficient? Knowing the authors, I strongly suspect that they are all necessary to get the suite of results. They don't add ingredients for show. But they want to match all of the impulse response functions, not just the inflation response. Perhaps a simpler set of ingredients could generate the inflation response while missing some of the others.
Let's understand what each of these ingredients is doing, which will help us to see (if) they are necessary and essential to getting the desired result.
I see a common theme in habit formation, adjustment costs that scale by investment growth, and indexation. These ingredients each add a derivative; they take a standard relationship between levels of economic variables and change it to one in growth rates. Each of consumption, investment, and inflation is a "jump variable" in standard economics, like stock prices. Consumption (roughly) jumps to the present value of future income. The level of investment is proportional to the stock price in the standard q theory, and jumps when there is new information. Iterating forward the new-Keynesian Phillips curve \(\pi_t = \beta E_t \pi_{t+1} + \kappa x_t\), inflation jumps to the discounted sum of future output gaps, \(\pi_t = E_t \sum_{j=0}^\infty \beta^jx_{t+j}.\)
To produce responses in which output, consumption and investment as well as inflation rise slowly after a shock, we don't want levels of consumption, investment, and inflation to jump this way. Instead we want growth rates to do so. With standard utility, the consumer's linearized first order condition equates expected consumption growth to the interest rate, \( E_t (c_{t+1}/c_t) = \delta + r_t \) Habit, with \(b=1\) gives \( E_t [(c_{t+1}-c_t)/(c_t-c_{t-1})] = \delta + r_t \). (I left out the strategic terms.) Mixing logs and levels a bit, you can see we put a growth rate in place of a level. (The paper has \(b=0.65\) .) An investment adjustment cost function with \(S(i_t/i_{t-1})\) rather than the standard \(S(i_t/k_t)\) puts a derivative in place of a level. Normally we tell a story that if you want a house painted, doubling the number of painters doesn't get the job done twice as fast because they get in each other's way. But you can double the number of painters overnight if you want to do so. Here the cost is on the increase in number of painters each day. Indexation results in a Phillips curve with a lagged inflation term, and that gives "sticky inflation." The Phillips curve of the model (32) and (33) is \[\pi_t = \frac{1}{1+\beta}\pi_{t-1} + \frac{\beta}{1+\beta}E_{t-1}\pi_{t+1} + (\text{constants}) E_{t-1}s_t\]where \(s_t\) are marginal costs (more later). The \(E_{t-1}\) come from the assumption that prices can't react to time \(t\) information. Iterate that forward to (33)\[\pi_t - \pi_{t-1} = (\text{constants}) E_{t-1}\sum_{j=0}^\infty \beta^j s_{t+j}.\] We have successfully put the change in inflation in place of the level of inflation.
The Phillips curve is anchored by real marginal costs, and they are not proportional to output in this model as they are in the textbook model above. That's important too. Instead,\[s_t = (\text{constants}) (r^k_t)^\alpha \left(\frac{W_t}{P_t}R_t\right)^{1-\alpha}\] where \(r^k\) is the return to capital \(W/P\) is the real wage and \(R\) is the nominal interest rate. The latter term crops up from the assumption that firms must borrow the wage bill one period in advance.
This is an interesting ingredient. There is a lot of talk that higher interest rates raise costs for firms, and they are reducing output as a result. That might get us around some of the IS curve problems. But that's not how it works here.
Here's how I think it works. Higher interest rates raise marginal costs, and thus push up current inflation relative to expected future inflation. The equilibrium-selection rules and the rule against instant price changes (coming up next) tie down current inflation, so the higher interest rates have to push down expected future inflation.
CEE disagree (p. 28). Writing of an interest rate decline, so all the signs are opposite of my stories,
... the interest rate appears in firms’ marginal cost. Since the interest rate drops after an expansionary monetary policy shock, the model embeds a force that pushes marginal costs down for a period of time. Indeed, in the estimated benchmark model the effect is strong enough to induce a transient fall in inflation.
But pushing marginal costs down lowers current inflation relative to future inflation -- they're looking at the same Phillips curve just above. It looks to me like they're confusing current with expected future inflation. Intuition is hard. There are plenty of Fisherian forces in this model that want lower interest rates to lower inflation.
More deeply, we see here a foundational trouble of the Phillips curve. It was originally a statistical relation between wage inflation and unemployment. It became a (weaker) statistical relation between price inflation and unemployment or the output gap. The new-Keynesian theory wants naturally to describe a relation between marginal costs and price changes, and it takes contortions to make output equal to marginal costs. Phillips curves fit the data terribly. So authors estimating Phillips curves (An
early favorite by Tim Cogley and Argia Sbordone) go back, and separate marginal cost from output or employment. As
CET write later, they "build features into the model which ensure that firms’ marginal costs are nearly acyclical." That helps the fit, but it divorces the Phillips curve shifter variable from the business cycle! Standard doctrine says that for the Fed to lower inflation it must soften the economy and risk unemployment. Doves say don't do it, live with inflation to avoid that cost. Well, if the Phillips curve shifter is "acyclical" you have to throw all that out the window.
This shift also points to the central conundrum of the Phillips curve. Here it describes the adjustment of prices to wages or "costs" more generally. It fundamentally describes a relative price, not a price level. OK, but the phenomenon we want to explain is the common component, how all prices and wage tie together or equivalently the decline in the value of the currency, stripped of relative price movements. The central puzzle of macroeconomics is why the common component, a rise or fall of all prices and wages together, has anything to do with output, and for us how it is controlled by the Fed.
Christiano Eichenbaum and Evans write (p.3) that "it is crucial to allow for variable capital utilization." I'll try explain why in my own words. Without capital adjustment costs, any change in the real return leads to a big investment jump. \(r=f'(k)\) must jump and that takes a lot of extra \(k\). We add adjustment costs to tamp down the investment response. But now when there is any shock, capital can't adjust enough and there is a big rate of return response. So we need something that acts like a big jump in the capital stock to tamp down \(r=f'(k)\) variability, but not a big investment jump. Variable capital utilization acts like the big investment jump without us seeing a big investment jump. And all this is going to be important for inflation too. Remember the Phillips curve; if output jumps then inflation jumps too.
Sticky wages are crucial, and indeed CEE report that they can dispense with sticky prices. One reason is that otherwise profits are countercyclical. In a boom, prices go up faster than wages so profits go up. With sticky prices and flexible wages you get the opposite sign. It's interesting that the "textbook" model has not moved this way. Again, we don't often enough write textbooks.
Fixing prices and wages during the period of the shock by assuming price setters can't see the shock for a quarter has a direct effect: It stops any price or wage jumps during the quarter of the shock, as in my first graph. That's almost cheating. Note the VAR also has absolutely zero instantaneous inflation response. This too is by assumption. They "orthogonalize" the variables so that all the contemporaneous correlation between monetary policy shocks and inflation or output is considered part of the Fed's "rule" and none of it reflects within-quarter reaction of prices or quantities to the Fed's actions.
Step back and admire. Given the project "find elaborations of the standard new-Keynesian model to match VAR impulse response functions" could you have come up with any of this?
But back to our task. That's a lot of apparently necessary ingredients. And reading here or CEE's verbal intuition, the logic of this model is nothing like the standard simple intuition, which includes none of the necessary ingredients. Do we really need all of this to produce the basic pattern of monetary policy? As far as we know, we do.
And hence, that pattern may not be as robust as it seems. For all of these ingredients are pretty, ... imaginative. Really, we are a long way from the Lucas/Prescott vision that macroeconomic models should be based on well tried and measured microeconomic ingredients that are believably invariant to changes in the policy regime.
CEE argue hard for the plausibility of these microeconomic specifications (see especially the later CET
Journal of Economic Perspectives article), but they have to try so hard precisely because the standard literature doesn't have any of these ingredients. The "level" rather than "growth rate" foundations of consumption, investment, and pricing decisions pervade microeconomics.
Microeconomists worry about labor monopsony, not labor monopoly; firms set wages, households don't. (
Christiano Eichenbam and Trabandt (2016) get wage stickiness from a more realistic search and matching model. Curiously, the one big labor union fiction is still the most common, though few private sector workers are unionized.) Firms don't borrow the wage bill a quarter ahead of time. Very few prices and wages are indexed in the US. Like habits, perhaps these ingredients are simple stand ins for something else, but at some point we need to know what that something else is. That is especially true if one wants to do optimal policy or welfare analysis.
Just how much economics must we reinvent to match this one response function? How far are we really from the ad-hoc ISLM equations that
Sims (1980) destroyed?
Sadly, subsequent literature doesn't help much (more below). Subsequent literature has mostly added ingredients, including heterogeneous agents (big these days), borrowing constraints, additional financial frictions (especially after 2008), zero bound constraints, QE, learning and complex expectations dynamics. (See
CET 2018 JEP for a good verbal survey.) The rewards in our profession go to those who add a new ingredient. It's very hard to publish papers that strip a model down to its basics. Editors don't count that as "new research," but just "exposition" below the prestige of their journals. Though boiling a model down to essentials is maybe more important in the end than adding more bells and whistles.
This is about where we are. Despite the pretty response functions, I still score that we don't have a reliable, simple, economic model that produces the standard view of monetary policy.
Mankiw and Reis, sticky expectations
Mankiw and Reis (2002) expressed the challenge clearly over 20 years ago. In reference to the "standard" New-Keynesian Phillips curve \(\pi_t = \beta E_t \pi_{t+1} + \kappa x_t\) they write a beautiful and succinct paragraph:
Ball [1994a] shows that the model yields the surprising result that announced, credible disinflations cause booms rather than recessions. Fuhrer and Moore [1995] argue that it cannot explain why inflation is so persistent. Mankiw [2001] notes that it has trouble explaining why shocks to monetary policy have a delayed and gradual effect on inflation. These problems appear to arise from the same source: although the price level is sticky in this model, the inflation rate can change quickly. By contrast, empirical analyses of the inflation process (e.g., Gordon [1997]) typically give a large role to “inflation inertia.”
At the cost of repetition, I emphasize the last sentence because it is so overlooked. Sticky prices are not sticky inflation. Ball already said this in 1994:
Taylor (1979, 198) and Blanchard (1983, 1986) show that staggering produces inertia in the price level: prices just slowly to a fall in th money supply. ...Disinflation, however, is a change in the growth rate of money not a one-time shock to the level. In informal discussions, analysts often assume that the inertia result carries over from levels to growth rates -- that inflation adjusts slowly to a fall in money growth.
As I see it, Mankiw and Reis generalize the Lucas (1972) Phillips curve. For Lucas, roughly, output is related to unexpected inflation\[\pi_t = E_{t-1}\pi_t + \kappa x_t.\] Firms don't see everyone else's prices in the period. Thus, when a firm sees an unexpected rise in prices, it doesn't know if it is a higher relative price or a higher general price level; the firm expands output based on how much it thinks the event might be a relative price increase. I love this model for many reasons, but one, which seems to have fallen by the wayside, is that it explicitly founds the Phillips curve in firms' confusion about relative prices vs. the price level, and thus faces up to the problem why should a rise in the price level have any real effects.
Mankiw and Reis basically suppose that firms find out the general price level with lags, so output depends on inflation relative to a distributed lag of its expectations. It's clearest for the price level (p. 1300)\[p_t = \lambda\sum_{j=0}^\infty (1-\lambda)^j E_{t-j}(p_t + \alpha x_t).\] The inflation expression is \[\pi_t = \frac{\alpha \lambda}{1-\lambda}x_t + \lambda \sum_{j=0}^\infty (1-\lambda)^j E_{t-1-j}(\pi_t + \alpha \Delta x_t).\](Some of the complication is that you want it to be \(\pi_t = \sum_{j=0}^\infty E_{t-1-j}\pi_t + \kappa x_t\), but output doesn't enter that way.)
This seems totally natural and sensible to me. What is a "period" anyway? It makes sense that firms learn heterogeneously whether a price increase is relative or price level. And it obviously solves the central persistence problem with the Lucas (1972) model, that it only produces a one-period output movement. Well, what's a period anyway? (Mankiw and Reis don't sell it this way, and actually don't cite Lucas at all. Curious.)
It's not immediately obvious that this curve solves the Ball puzzle and the declining inflation puzzle, and indeed one must put it in a full model to do so. Mankiw and Reis (2002) mix it with \(m_t + v = p_t + x_t\) and make some stylized analysis, but don't show how to put the idea in models such as I started with or make a plot.
Their less well known follow on paper Sticky Information in General Equilibrium (2007) is much better for this purpose because they do show you how to put the idea in an explicit new-Keynesian model, like the one I started with. They also add a Taylor rule, and an interest rate rather than money supply instrument, along with wage stickiness and a few other ingredients,. They show how to solve the model overcoming the problem that there are many lagged expectations as state variables. But here is the response to the monetary policy shock:
 |
| Response to a Monetary Policy Shock, Mankiw and Reis (2007). |
Sadly they don't report how interest rates respond to the shock. I presume interest rates went down temporarily.
Look: the inflation and output gap plots are about the same. Except for the slight delay going up, these are exactly the responses of the standard NK model. When output is high, inflation is high and declining. The whole point was to produce a model in which high output level would correspond to rising inflation. Relative to the first graph, the main improvement is just a slight hump shape in both inflation and output responses.
Describing the same model in "Pervasive Stickiness" (2006), Mankiw and Reis describe the desideratum well:
The Acceleration Phenomenon....inflation tends to rise when the economy is booming and falls when economic activity is depressed. This is the central insight of the empirical literature on the Phillips curve. One simple way to illustrate this fact is to correlate the change in inflation, \(\pi_{t+2}-\pi_{t-2}\) with [the level of] output, \(y_t\), detrended with the HP filter. In U.S. quarterly data from 1954-Q3 to 2005-Q3, the correlation is 0.47. That is, the change in inflation is procyclical.
Now look again at the graph. As far as I can see, it's not there. Is this version of sticky inflation a bust, for this purpose?
I still think it's a neat idea worth more exploration. But I thought so 20 years ago too. Mankiw and Reis have a lot of citations but nobody followed them. Why not? I suspect it's part of a general pattern that lots of great micro sticky price papers are not used because they don't produce an easy aggregate Phillips curve. If you want cites, make sure people can plug it in to Dynare. Mankiw and Reis' curve is pretty simple, but you still have to keep all past expectations around as a state variable. There may be alternative ways of doing that with modern computational technology, putting it in a Markov environment or cutting off the lags, everyone learns the price level after 5 years. Hank models have even bigger state spaces!
Some more models
What about within the Fed? Chung, Kiley, and Laforte 2010, "Documentation of the Estimated, Dynamic, Optimization-based (EDO) Model of the U.S. Economy: 2010 Version" is one such model. (Thanks to Ben Moll, in a lecture slide titled "Effects of interest rate hike in U.S. Fed’s own New Keynesian model") They describe it as
This paper provides documentation for a large-scale estimated DSGE model of the U.S. economy – the Federal Reserve Board’s Estimated, Dynamic, Optimization- based (FRB/EDO) model project. The model can be used to address a wide range of practical policy questions on a routine basis.
Here are the central plots for our purpose: The response of interest rates and inflation to a monetary policy shock.
No long and variable lags here. Just as in the simple model, inflation jumps down on the day of the shock and then reverts. As with Mankiw and Reis, there is a tiny hump shape, but that's it. This is nothing like the Romer and Romer plot.
Smets and Wouters (2007) "Shocks and Frictions in US Business Cycles: A Bayesian DSGE Approach" is about as famous as Christiano Eichenbaum and Evans as a standard new-Keynesian model that supposedly matches data well. It "contains many shocks and frictions. It features sticky nominal price and wage settings that allow for backward inflation indexation, habit formation in consumption, and investment adjustment costs that create hump-shaped responses... and variable capital utilization and fixed costs in production"
Here is their central graph of the response to a monetary policy shock
Again, there is a little hump-shape, but the overall picture is just like the one we started with. Inflation mostly jumps down immediately and then recovers; the interest rate shock leads to future inflation that is higher, not lower than current inflation. There are no lags from higher interest rates to future inflation declines.
The major difference, I think, is that Smets and Wouters do not impose the restriction that inflation cannot jump immediately on either their theory or empirical work, and Christiano, Eichenbaum and Evans impose that restriction in both places. This is important. In a new-Keynesian model some combination of state variables must jump on the day of the shock, as it is only saddle-path stable. If inflation can't move right away, that means something else does. Therefore, I think, CEE also preclude inflation jumping the next period. Comparing otherwise similar ingredients, it looks like this is the key ingredient for producing Romer-Romer like responses consistent with the belief in sticky inflation.
But perhaps the original model and Smets-Wouters are right! I do not know what happens if you remove the CEE orthogonalization restriction and allow inflation to jump on the day of the shock in the date. That would rescue the new-Keynesian model, but it would destroy the belief in sticky inflation and long and variable lags.
Closing thoughts
I'll reiterate the main point. As far as I can tell, there is no simple economic model that produces the standard belief.
Now, maybe belief is right and models just have to catch up. It is interesting that there is so little effort going on to do this. As above, the vast outpouring of new-Keynesian modeling has been to add even more ingredients. In part, again, that's the natural pressures of journal publication. But I think it's also an honest feeling that after Christiano Eichenbaun and Evans, this is a solved problem and adding other ingredients is all there is to do.
So part of the point of this post (and "Expectations and the neutrality of interest rates") is to argue that this is not a solved problem, and that removing ingredients to find the simplest economic model that can produce standard beliefs is a really important task. Then, does the model incorporate anything at all of the standard intuition, or is it based on some different mechanism al together? These are first order important and unresolved questions!
But for my lay readers, here is as far as I know where we are. If you, like the Fed, hold to standard beliefs that higher interest rates lower future output and inflation with long and variable lags, know there is no simple economic theory behind that belief, and certainly the standard story is not how economic models of the last four decades work.
Update:
I repeat a response to a comment below, because it is so important.
I probably wasn't clear enough that the "problem" of high output with inflation falling rather than rising is a problem of models vs. traditional beliefs, rather than of models vs. facts. The point of the sequence of posts, really, is that the traditional beliefs are likely wrong. Inflation does not fall, following interest rate increases, with dependable, long, and perhaps variable lags. That belief is strong, but neither facts, empirical evidence, or theory supports it. ("Variable" is a great way to scrounge data to make it fit priors.) Indeed many successful disinflations like ends of hyperinflations feature a sigh of relief and output surge on the real side.







I believe the Romer & Romer graphs measure the lags from the start of a Fed hiking cycle, not from an individual interest rate change. It’s not clear to me whether they lag effect is caused by that initial change in expectations or the actual subsequent interest rate hikes.
ReplyDeleteActually, I think it's the opposite. Romer and Romer look for the date when the Fed finally gets fed up with inflation and does something dramatic about it, but many of their dates are surprisingly late in the hiking cycle.
DeleteSelf-advertisement, but for more of the economics/history of thought on the failure to adopt sticky wage models: https://basilhalperin.com/essays/sticky-prices-vs-sticky-wages.html
ReplyDeleteBasil's post is excellent! Go read it. I'll emphasize one of his many good points, because I think it's the most under appreciated. In evaluating macroeconomic models, a lot of thinking is governed by "what explains the features of business cycles?" for example the correlation of real wages with output. Facts like those undermined the sticky wage view. But once we recognize that only very small fractions of business cycles are due to monetary policy shocks, then model ingredients that account for the partial effect of monetary policy are not well judged by model ingredients that explain business cycle correlations. "Explaining business cycles" and "understanding the partial effects of monetary policy" are now two different questions. In micro, if you want to understand the partial effect of a supply curve shift, understanding raw correlations between prices and quantities from data in which both supply and demand moved is not useful. The implicit assumption that business cycles are all due to monetary mistakes is wrong.
DeleteInteresting post.
ReplyDeleteTypo?:
ReplyDelete"This is not a new issue. Larry Ball (1994) first pointed out that the standard new Keynesian Phillips curve says that inflation [think that should be "output"?] is high when inflation is high relative to expected future inflation, that is when inflation is declining. Standard beliefs go the other way: output is high when inflation is rising."
(Nick Rowe)
"This is not a new issue. Larry Ball (1994) first pointed out that the standard new Keynesian Phillips curve says that output is high when inflation is high relative to expected future inflation, that is when inflation is declining."
ReplyDeleteDoes this not basically describe where we are right now? Output is high, inflation is falling.
I probably wasn't clear enough that the "problem" of high output with inflation falling rather than rising is a problem of models vs. traditional beliefs, rather than of models vs. facts. The point of the post, really, is that the traditional beliefs are likely wrong. Indeed most successful disinflations like ends of hyperinflations feature a sigh of relief and output surge on the real side.
DeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
DeleteAs a layman, I can always get through about 1/4 of Pr. Cochrane's articles before my eyes cross and cut to the chase in the summary. That said, a few observations. First, the struggle to make the Phillips Curve and Keynesian modeling work seem like the geo-centric model of the solar system that had all those tortured modifications (retrograde orbits, etc.) added to make it work and was ultimately replaced by the simpler helio-centric model we use today. Good application of Ockam's Razor, which is likely sorely needed here.
ReplyDeleteNext, as a business person I can say wages are much stickier than prices and costs. The cycle goes something like this. We get notified of a price increase from a vendor. We try to negotiate it away, reduce it or delay it. While this is going on, we raise prices immediately. Nice arbitrage and profits rise in the short term. Then the cost increases take hold and we look to cut expenses to maintain the same profit level.
When we look at wages, we can't for many reasons reduce individuals' wages without causing a panic. So our first tactic is to let natural attrition reduce payroll expense. If that is insufficient, make a handful of positions "redundant" and eliminate them. At year end, perhaps we give a COLA raise, which is less than the actual COLA, and get an arbitrage there. When all else fails, we make layoffs, which can be pretty indiscriminate.
On the flip side, we resist accross the board raises because you can't claw them back like you can with prices/costs without that huge disruption to the workforce.
Bottom line is individual wages really can't be considered like prices/costs which operate at the unit level and likely contribute to that "long and variable lag" effect.
Thanks for this great comment. While writing thousands of papers about price stickiness economists often don't just ask business people how they set prices and wages! I often advise grad students modeling this or that behavior, "did you go out and ask people?"
DeleteHonestly, this all comes across like alchemy. Very complicated with many many assumptions and no data to back up anything.
ReplyDeleteIf I were in your position, I would suggest trying to come up with very very basic "laws" that are highly predictive of *SOMETHING*. Things like Newton's basic laws of motion or Euclids basic theorems. Once you can predict SOMETHING you can build on it. But without being able to predict anything at all, it is probable that the entire conceptual system you've build is worthless. After all, the worth of a model is its abiltiy to predict.
I would start with basic things:
- Prices are linearly related to quantity of money
- Prices are related to a shift from savings to spending.
- "Savings" can be identified as activities that do not drive up demand, and thereby, prices.
- Econmic reactions take time
- A rise in interest rates has a net effect of adding/subtracting from the money supply
- Persistent higher/lower interest rates have the long term net effect of adding/subtracting to the money supply.
- People will work more when they are poor.
- People will invest more when they are wealthy.
- People will spend more when they are wealthy.
- People will save more when they are wealthy/poor
I think if you figure out the data behind basic concepts such as the above, you'll be able to build to something that predicts inflation pretty well.
Putting some numbers around these will do a much better job.
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteOk. Here goes. I'm commenting as both a person who "drank the kool-aid" of economics (cherry flavor), with a bit of indigestion, and as someone who also works in mental health, and still works in tech, trying to build stuff that generates efficiency gains.
ReplyDeleteFirst, here is an article that all econometricians and statistics gurus should take to heart:
https://www.worldeconomicsassociation.org/newsletterarticles/econometric-models-wrong/
Some gems mined from this geode:
“Since econometrics does not content itself with only making optimal predictions, but also aspires to explain things in terms of causes and effects, econometricians need loads of assumptions — most important of these are additivity and linearity. Important, simply because if they are not true, your model is invalid and descriptively incorrect. And when the model is wrong — well, then it is wrong.”
“Real-world social systems are not governed by stable causal mechanisms or capacities. The kinds of ‘laws’ and relations that econometrics has established, are laws and relations about entities in models that presuppose causal mechanisms being atomistic and additive. When causal mechanisms operate in real-world systems they only do it in ever-changing and unstable combinations where the whole is more than a mechanical sum of parts. If economic regularities obtain they do it (as a rule) only because we engineered them for that purpose. Outside man-made ‘nomological machines’ they are rare, or even non-existent. Unfortunately, that also makes most of the achievements of econometrics – as most of the contemporary endeavours of mainstream economic theoretical modelling — rather useless.”
There are more to mine.
However, I’m constructing an attack vector based on a different premise altogether: Econometric models that use P on the Y-axis, with Q on the X-axis are inadvertently (ha) – and it also doesn’t matter if it’s time-series/longitudinal – are missing important what I call ‘noetic factors” that add explanatory power to understanding economic phenomena.
After all, it’s people who live and function in an economy. Trying to use P or money as an encoding mechanism that globs these factors together turns econometrics into Sisyphantic condition. That might sound really weird philosophically, but premises do matter.
My own whittling of the gnarly wood to fashion a stake is to not so much kill the vampire, but release it from its own hunger of desperation:
“Due to the subjective nature of valuation itself, currency, when exchanged, only captures what is seen in the value of work itself: time and effort. It says absolutely nothing about the factors that allow one to produce anything a priori to time and effort: One has to make the choice to engage in such activities first AND be in a functional position to do so, both physically and mentally. The rational and irrational cognitive activities that occur through some unknown and mysterious time horizon, while also fueled by needs and desires (demand), produce a condition that culminates in a person deciding to use their own (L)[energy(amt_x) with time(amt_x)], along with (K)[tools, physical resources], to produce something, what we’ll call good_y(Q). This is a re-expression/re-formulation of a production function. The underlying point I’m attempting to highlight here is that using econometric models will always lose something because money only encodes valuation at a certain point in time, as it does not consider all the previous events that leads one to ‘have’ some quantity of variable goods with some value attached to them.”
Continued...
(from previous rant - continuing on):
ReplyDeleteSo what does any of this have to do with economics? Well, economies are systems in the end, with numerous individual and supposedly “rational” agents – we call them humans. Sure, BE has attempted to shine light on this idealism as being flawed, in the attempt to make policy formation more compassionate to the realities of living as a human being on planet earth and making decisions in the context of scarcity. Scarcity as a given isn’t enough, and even realizing tradeoffs aren’t enough. We have to get to the why beyond 2 dimensional Maslow Pyramids.
Some may argue that prices are enough to encode relative scarcity, that all the variance of human behavior is somehow accounted for in the functioning of the economy: Do I really care beyond the price of my car how stable the economy is? Probably not, but if inflation hits durable goods, I care that the price of the car before was x and now it is x + (some scalar)*x.
The Fed is supposed to be the adult in the room in what is functionally kindergarten. The fiscal side might as well resemble an asylum.
What’s the way out? I believe that analysis requires an equilibrium of objective quantitative data along with subjective qualitative data (the attempt to make noetic data NOT noetic – think psychological tests which seek to make the unquantifiable quantifiable). After all, if optimization is supposed to be a straight-forward process, at least mathematically, I think we’re finding some – or maybe all of them – are not only wrong but have lost some of their usefulness.
I hope one doesn’t get the idea it’s all useless. It is not. We are forever on a path of improvement towards something resembling stability and harmony. The alternative is to succumb to chaos, which is really a non-starter.
Physicists don't have a good theory for gravity, but they're pretty sure it's there and what it does. Until economists can model interest rate interventions with some precision, let them rather stick to what those interventions do.
ReplyDeleteThis is a strange comment, is your advice to physicists to give up on a unified theory and stick to mutually inconsistent models that appear to work for certain specific things? Physicists spend a lot of effort on coming up with a unified consistent theory of those things they are sure are there but can't entirely explain...so do economists.
DeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteCPI and price indices generally are illogical. For lack of a better comparison, price indices are similar to 3 body problems where the same inputs can lead to dramatically different outputs depending on the state of the economic system. The price indices are a result of two primary interactions: aggregate demand vs aggregate supply & the amount of money (base and credit). However, even worse they only measure some AD vs AS- focused primarily on consumption and ignoring asset prices.
ReplyDeleteCPI and price indices might be beneficial for vaguely comparing quality of life across time or even total output across time, but clearly central bankers using them as if the target was carved in stone makes limited sense. The working class and populists do not have nearly enough contempt for the expert economists and central bankers. Even a child would understand these simple facts. Therefore, we are left with the only explanation being misaligned incentives and malice to explain why economists and bankers pull the wool over society’s eyes by speaking of such nonsense as CPI targeting and related moronic concepts like r*, etc.
It is no wonder that as this series has demonstrated CPI theory and facts do not align.
As L Talbert, Mykel and Fish mention above there are many simple ways macro economics could be improved. Binning CPI as a target for central banks would go a long way to improving economics and social outcomes.
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteModels try to quantify our intuitive understandings of the world which are shaped by our experience. I see the failure of NK models to map theory onto data as a failure of the academy, not a failure of the intuitive "higher interest rates lower inflation via a contraction in investment then employment etc.".
ReplyDeleteYou write at the end that, "The point of the sequence of posts, really, is that the traditional beliefs are likely wrong. Inflation does not fall, following interest rate increases, with dependable, long, and perhaps variable lags." I think this is precisely backwards, that models cannot capture the mechanisms behind the traditional beliefs in a credible way that maps to the data, but that the traditional beliefs are still more true than not. You're all using a new kind of rational expectations math that was invented in 1976 and that you're trying to fit to 80 years of highly variable data. It's no surprise you're doing a terrible job as a profession.
PS: not sure how fair calling them "traditional beliefs" is, makes them seem relegated to a hokey backwater of irrelevance rather than most of the world's central banks.
Economics, as Fisher said, is an exact science. The fact is, banks don't lend deposits, so all bank-held savings are frozen.
ReplyDeleteThe federal deficit is a time bomb. The award rate on O/N RRPs is 5.30% for $1,574.065 on 9/1/23. The rate on 3mo T-bills is higher. Thus, funds have come out of the O/N RRP.
ReplyDeleteThere’s been a $734b drawdown since 4/24. That’s not a liability swap (removing cash from the FED). If that’s what it takes to fund the Treasury’s tsunami, then interest rates would have risen further without that funding source?
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteThe mechanism by which the Fed raises or lowers rates is by expanding or contracting the cash and debt supply. Raising rates is done by contracting the cash supply in private hands, and raising the supply of debt. Lowering rates is done by expanding the cash supply and lowering the supply of debt in private hands.
ReplyDeleteThe impact on inflation is a function not of the rate change, but of the change in the levels of supply of debt and cash in the economy. The relationship between the % of the cash supply outstanding that needs to be printed to lower interest rates is probably not linear at all.
Because treasuries can be used in many ways just like cash, it's not clear that more debt in private hands has much of a different effect than more cash in private hands. When interest rates hit zero, they are probably equivilant, while when rates are high, debt in private hands will lead to long-run expansion of the cash supply and inflation.
You get the picture. The first-order equations don't link inflation and rates. Rather, the first-order relationships concertn changes in the supply of debt and cash with both of those.
The data are much more clearer if you look at market data (and not lagging Fed Funds). The fed prepares the market that it will act. Take as an example the 10 Yr Treasury and the 10 yr Breakeven Inflation Rates: Breakeven passes 2% end of December 2020 and had their peak in April 2022. 10 yr Treasury minus 10 yr Breakeven (=real rates) started climbing end of 2021, which means financial conditions tightened since then. CPI ex energy had the peak in September 2022, which seems a reasonable lag of 9 months.
ReplyDeleteCouldn't a much simpler theory allowing for long-term debt and varying levels of access to credit across consumers and firms explain how monetary shocks would transmit with a lag?
ReplyDeleteI was tinkering the other night because I was curious if I could build an economic framework for confirming Dr. Cochrane's position about inflation seeing an uptick once perceived and then melts away on its own. I managed to use the Marginal Utility of an Extra Dollar and how inflation exacerbates that, leading to an uptick in short term consumption until the fuel runs out, by a blend in reduction in M and inflating prices. It can then feed into larger economic trends. It's actually not that complex either, as the components include consumer theory and FV = PV(1 + r)^t where t equals number of periods. Then it can get overlayed onto AD/AS graphs which can help explain shifts in the price level based on these insights. It's not magical math, but if you believe Galbraith, economic forecasting/modeling is no better than astrology.
ReplyDeleteI'm gonna excel it out. Should be interesting. There's a sort of satisfaction in playing around and blending concepts in economics. It's like working with colors of paint. You mix and swirl them around and hopefully something discernable and consumable emerges.
There's always the latent doubt I'm wrong or insane but the whole practice is fun, interesting, and the other hope is maybe someone will use the stuff that Dr. Cochrane generates (mine is just entertainment, ha!)to have better outcomes instead of perpetual chaos. That's the dream.
Unless savings are expeditiously activated, put back to work in the circular flow of income, a dampening economic impact is generated. What the economy needs is high real rates of interest combined with a high money velocity. The U.S. Golden Era in Capitalism is prima facie evidence, where 2/3 of the economy was financed by velocity.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteIsn't the standard keynesian model more like a proof of concept in order to establish rough correlations? More complicated models, such as Christiano et al, provide a more detailed description of reality with more accurate lag structures? My point is that isn't it a little bit unfair to crititize the three equation NKM, even though in practice central banks think in terms of more complicated models?
ReplyDeleteVery interesting thread!
ReplyDeleteAs you wrote, prof. Cochrane, econometric procedures identify monetary policy (MP) shock and the response to it. However, MP surprises or mistakes are not the main source of interest rate variation. MP is a stabilization tool, most of its variation comes from Taylor rule, not from its disturbance (or, to put it differently: it represent movements along the AD curve, not shifts to the AD curve). And importantly - it is communicated and perceived by people a such. When FOMC increases interest rates by 25bp people see the increase by 25bp and react appropriately, they are not filtering out how much is a surprise. I'm not aware of any paper calculating what is the contribution of a stabilization part of the MP to business cycle. And the reaction or contribution of surprise shocks may not give the proper answer, at least when one belies in Lucas distinction of expected and unexpected components of MP.
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteI’ll just keep believing that lower rates help moderate inflation by boosting growth. Ultimately, inflation has nothing to do with rates, but rather it’s just deficit spending exceeding the rate of growth.
ReplyDelete